들어가며
이 문제는 BFS를 알면 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
코드
public class 백준2606_바이러스 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> arr = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
int n = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
int k = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
arr.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i <k; i++){
String[] input = reader.readLine().split(" ");
int start = Integer.parseInt(input[0])-1;
int end = Integer.parseInt(input[1])-1;
arr.get(start).add(end);
arr.get(end).add(start);
}
queue.add(0);
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
visited[0] = true;
int result = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int current = queue.poll();
result++;
for (var next : arr.get(current)) {
if (!visited[next]) {
visited[next] = true;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
System.out.println(result-1);
}
}풀이법
BFS는 그래프나 트리에서 시작 노드부터 가까운 노드를 우선적으로 탐색하는 알고리즘이다.
큐(Queue) 나 재귀 함수를 사용하여 그래프의 정점들을 계층적으로 탐색한다.
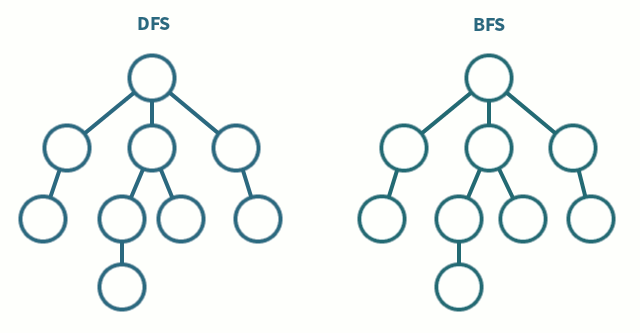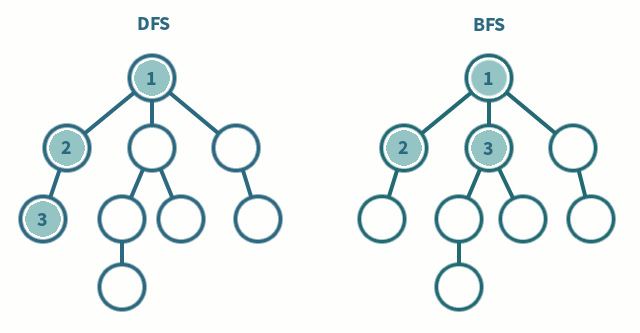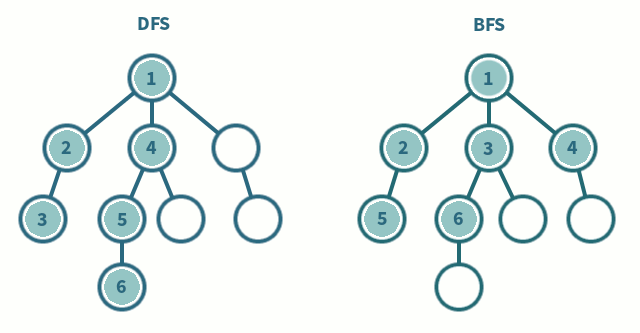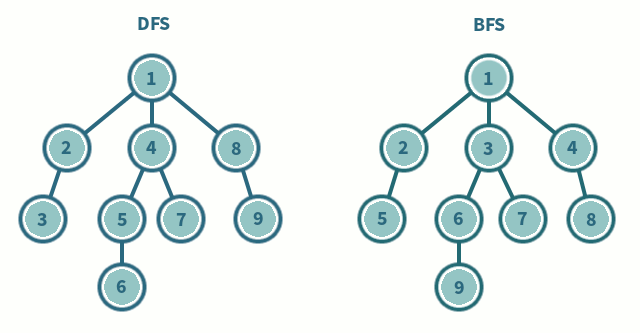
이 문제에선 Queue를 사용하여 BFS를 구현하는 방식으로 구현했다.
또한 그래프의 표현에 있어 인접리스트를 사용하여 무방향 그래프를 구현했다.

인덱스를 1부터 시작해도 되지만, 배열은 보통 0에서 시작하니까 0을 시작점으로 맞춰주었다.
Queue는 맨 앞에 있는 것부터 꺼낸다. 이런 특성을 이용한 것인데, 한 노드에 도착하면 인접 행렬에 넣어진 노드들을 모두 넣는다.
그러면 순서대로 들어갈텐데, 다시 큐에서 맨 앞에 있는 노드부터 하나씩 뺀다.
그렇게 인접 노드를 우선으로 탐색이 진행되서 BFS가 되는 것이다.
참고 자료
'알고리즘 문제 풀이 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준]11047 - 동전 0 문제 풀이(Java,자바) (1) | 2025.01.26 |
|---|---|
| [백준]9095 - 1, 2, 3 더하기 문제 풀이(Java,자바) (0) | 2025.01.13 |
| [백준]1463 - 1로 만들기 문제 풀이(Java,자바) (2) | 2025.01.07 |
| [백준]1620 - 나는야 포켓몬 마스터 이다솜 문제 풀이(Java,자바) (0) | 2025.01.07 |
| [백준]1764 - 듣보잡 문제 풀이(Java,자바) (0) | 2025.01.07 |